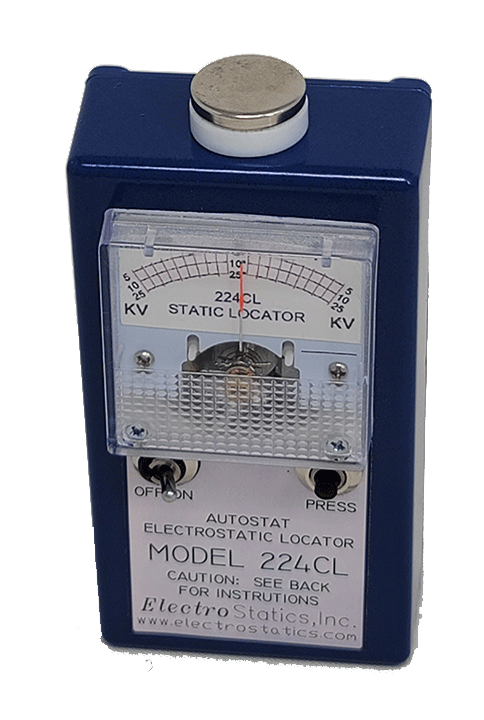
Static electricity: What it is and how to eliminate
Static Electricity and Static Control removal: Technical Overview and Ionization Systems
Static electricity control is essential in modern manufacturing, electronics, and packaging industries where electrostatic charge can cause ESD damage, dust attraction, or process interruptions. Understanding how static electricity is generated—and how to neutralize it—is key to maintaining product quality and safety.
Using ionization systems, anti-static bars, and grounding equipment, static charge can be effectively eliminated from non-conductive materials such as plastic, paper, and glass. Electrostatics.com provides advanced industrial static control solutions designed to measure, neutralize, and prevent electrostatic discharge across a wide range of applications. Whether you need ESD protection for electronics assembly or static eliminators for converting lines, ionization offers the most reliable method to restore charge balance and improve process efficiency.
Technical Overview of Electrostatic Phenomena, ESD Protection, and Ionization Systems for Industrial applications needing to control Static Electricity to add or remove reduce or eliminate
Introduction to Static Electricity:
This article provides a detailed technical explanation of static electricity and proven methods to measure, neutralize, and eliminate electrostatic charge in industrial and electronic environments. It addresses key engineering and process-control questions such as:
What is static electricity and how is it generated?
How does electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage components and materials?
What causes charge buildup on plastics, paper, and glass and like materials?
How can static electricity be neutralized using industrial ionizers and anti-static equipment?
What best practices ensure effective static control in manufacturing processes?
Understanding the causes and control of static charge is essential for improving product quality, reducing downtime, and preventing ESD-related failures.
What Is Static Electricity?
Static electricity (also called electrostatic charge or static electric charge) is an imbalance of electric charge (positive and/ or negtive charges) on the surface or within a material. Unlike current electricity, which involves continuous electron flow through a conductor, static electricity represents electricity at rest. Static electricity can be a positive or a negitive charge.
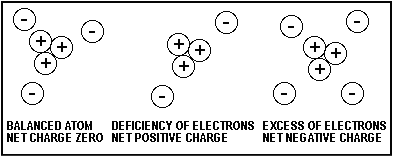
Charge generation commonly occurs through:
Triboelectric charging – contact and separation between dissimilar materials
Induction – charge redistribution due to nearby electric fields
Conduction – direct charge transfer between conductive surfaces
The polarity (positive or negative static charges) and magnitude ( usually in Kilovolts) of static charge depend on material composition, surface resistivity, electrical condutivity, humidity, and environmental conditions. When the electrostatic potential difference between objects exceeds the dielectric strength of air, a static discharge occurs — known as electrostatic discharge (ESD).
Example: Atmospheric Electrostatics and Lightning
A large-scale example of static electricity is lightning. In the atmosphere, static charge builds within clouds due to particle collisions and friction. When the electric field strength exceeds approximately 3 megavolts per meter, air — normally an insulator — breaks down, resulting in a high-current discharge.
This process demonstrates how static electricity transitions into dynamic electricity to neutralize charge imbalance. On a smaller scale, similar discharges occur when you touch a door knob and feel a shock. It also happens in industrial and electronic systems, where uncontrolled static buildup can cause costly ESD damage, attract contamination, cause operator shocks.
Industrial Impact of Static Electricity
Uncontrolled static electricity can create significant problems in industrial environments, including:
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage to sensitive electronic components
Dust and particle attraction, causing contamination on film, plastic, and paper webs
Process interruptions due to static adhesion, mis-feeds, or jams
Ignition hazards in environments with flammable vapors or powders
Operator shock safety and productivity issues for the workforce
The financial impact of static-related issues is measured in billions of dollars annually across industries such as electronics manufacturing, medical device manufacturing packaging, converting, plastic manufacturing, and printing.
How to control or remove static electricity and Anti static Methods
See special issues with a moving web of material and static electricity.
Effective static control systems combine both charge prevention and active neutralization strategies. Common methods include:
Grounding and Bonding:
Provides a conductive path to safely dissipate electrostatic charge from equipment and personnel. This method is effective with conductive materials.Environmental Control:
Maintaining proper humidity levels increases surface conductivity and reduces charge accumulation. This is an expensive way to reduce static electricity and can lead to heath concern with mold and mildew.Ionization Systems:
Industrial ionizers (also called static eliminators or anti-static ionizers static bars anti static blowers) produce balanced streams of positive and negative ions that neutralize static charges on insulating materials such as plastic, glass, and paper.
Types include AC corona ionizers, DC ionizers, pulsed DC ionizers, and plasma ionizers. Of these methods AC corona ionizers, DC ionizers are the most reliable and cost effective.
These systems are essential in clean rooms, converting lines, medical device manufacturing and packaging, printing, circuit board manufacturing, packaging areas, and ESD-safe environments.
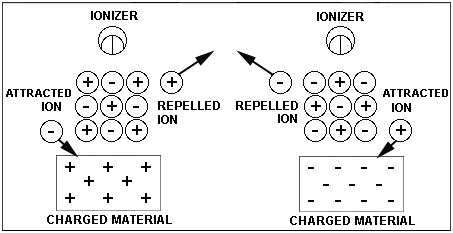
- Anti-Static Materials and Coatings:
Incorporating conductive fillers, carbon loading, or surface treatments helps reduce triboelectric charging. This coating or material change can be expensive and may not be possible depending on the end use such as material used in a medical device.
- Measurement and Monitoring:
Electrostatic field meters, charge plate monitors, and ion balance testers provide quantitative data for process verification and equipment calibration.Applications of Static Control and Ionization Equipment
Static control solutions are critical in many industries, including:
Electronics assembly and semiconductor manufacturing (ESD protection)
Plastic film extrusion, bagging, and thermoforming (static neutralization)
Printing and converting (web cleaning and dust control)
Pharmaceutical and medical packaging (particle attraction prevention and removal)
Circuit board manufacturing cleaning layer of copper and dielectric
Powder coating and materials handling (ignition hazard reduction)
Using high-performance ionization equipment and anti-static bars ensures consistent static elimination and process reliability.
Conclusion
Understanding static electricity in manufacturing and applying the correct control measures is essential to safeguard product quality, reduce downtime, and improve worker safety. By integrating grounding, ionization systems, anti-static equipment, and monitoring tools, manufacturers in medical devices, semiconductors, and automotive industries can efficiently eliminate static, prevent ESD events, and maintain clean, reliable operations.
Category Solutions:
Static Bars | Ionizing Blowers | Anti static blow off air guns|Static Meters | Web Cleaners
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What causes static electricity in industrial environments?
Static electricity is typically generated through triboelectric charging, which occurs when two dissimilar materials contact and separate, causing electron transfer. In manufacturing, this happens with plastic films, paper webs, textiles, and conveyors. Low humidity, high-speed processes, and non-conductive materials increase charge accumulation, leading to electrostatic discharge (ESD) and contamination issues.
2. How do ionization systems eliminate static electricity?
Ionization systems (also called static eliminators or anti-static ionizers) produce balanced streams of positive and negative ions that neutralize surface charge on insulating materials. The ions recombine with charged areas, restoring electrical balance. Industrial ionizers include AC corona, DC, and pulsed DC ionizers, often used in packaging, converting, and electronics assembly environments.
3. What is the best way to remove static charge from plastic, paper, and glass?
To remove static charge from non-conductive materials such as plastic, paper, and glass, use industrial ionization equipment in combination with proper grounding and humidity control. Ionizers continuously neutralize charge buildup, while grounding systems dissipate charge safely from conductive machinery and personnel. This integrated approach ensures consistent static control and ESD protection.
4. How does static electricity cause electrostatic discharge (ESD)?
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) occurs when a charged object contacts or comes close to another object with a different potential, allowing electrons to flow rapidly and equalize the imbalance. Even low-level discharges can damage semiconductors, sensors, and printed circuit boards, making ESD control systems essential in electronics manufacturing and clean rooms.
5. What are the most effective static control products for industrial applications?
Effective static control products include:
Ionization bars and blowers – neutralize static on moving materials
Grounding and bonding systems – provide discharge paths for conductive objects
Anti-static films and coatings – minimize charge buildup on surfaces
Electrostatic field meters – measure charge levels for process monitoring
Combining these technologies ensures reliable static elimination and enhanced process efficiency.
|
Broad area static control and reduces operator shocks. A big anti static machine. Also available with balance circuit for large area ESD applications
|
Watch static electricity pin sheets to a grounded surface |
 Ionization Nozzles Part blow off and pin point static control. |
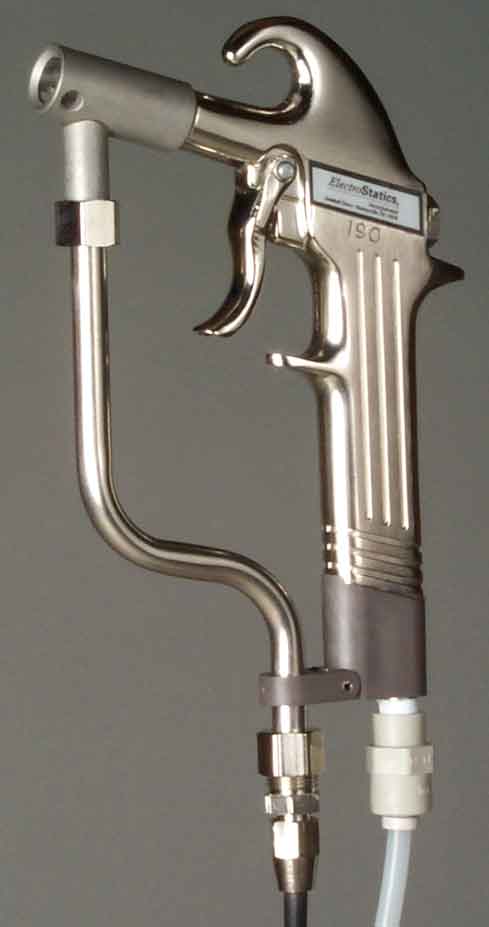 Anti Static Control Blow off Gun Ionizing air gun |
Watch air blow off vs Anti static air blow off gun
ESD protection, Part blow off, pin point static control |
|
Static control for webs and sheets of plastic, paper glass or other non conductive material |
Overhead ionizer ESD protection and light duty static control |
|
Table Top
Ionizer |
 |
|
Remove static and actively clean a surface |
| static electricity |

ElectroStatics, Inc.
63 East Broad Street - Suite 6, Hatfield, PA 19440
Tel: (215) 513-0850 FAX: (215) 513-0855
Websites: electrostatics.com & www.webcleaning.com
©1996-2026 Electrostatics Incorporated